PSORIASIS
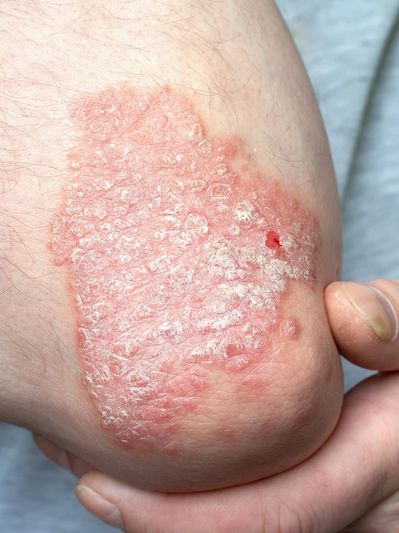
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune skin disorder which affects 2-3% of the global population. The condition is attributed to rapid skin cell turnover which results in thick, scaly patches of skin which are uncomfortable and painful.
Current treatments for psoriasis include topical therapies such as corticosteroids, phototherapy, and systemic agents like cyclosporine. While these approaches can be effective in managing symptoms, long-term use carries notable risks.
Recently, there have been some significant advancements in treatment of moderate to severe Psoriasis with a number of systemic antibody therapies significantly improving the lives of patients. Although a step change in the treatment of psoriasis, there is still the need for new non-steroidal topical treatments as combination or adjunct therapies in psoriasis.